Pediatric heart failure may be defined as a state in which the heart fails in its primary role of circulating blood throughout the body. This might lead to serious complications if not detected early. Heart failure in children may not be immediately apparent until the condition worsens. This may be attributed to the early detection of the warning signs associated with the condition.
“Since pediatric or infant heart failure can be a subtly developing condition, it is crucial for parents and caregivers to be vigilant and monitor their child’s health for signs such as fatigue and rapid breathing,” states Dr. Prashant Bobhate, a leading pediatric cardiologist in Mumbai. “If appropriately managed and treated, children with heart failure can lead a normal and healthy life.

With over 12 years of experience in his field, Dr. Bobhate specializes in the management of pediatric heart failure in Mumbai, combining cutting-edge diagnostics with personalized treatment plans to ensure the best care for children at Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital. He is well-versed in dealing with both congenital and acquired conditions of the heart and is thus a professional of high repute for managing infant heart failure.
Wondering what pediatric heart failure is and how it affects children? Here’s an overview of this serious condition.
What is Pediatric Heart Failure?
Pediatric heart failure occurs when a child’s heart is unable to pump blood efficiently, leading to insufficient blood flow to organs and tissues. It can be caused by congenital heart defects, infection, cardiomyopathy, or other heart-related conditions. Symptoms of pediatric heart failure can vary but often include fatigue, rapid breathing, and swelling. Timely intervention is crucial, as untreated heart failure can lead to long-term complications or even life-threatening conditions.
How to spot the early signs of pediatric heart failure? Let’s explore the top warning signs you should look out for in your child.
Warning Sign 1: Unexplained Fatigue and Weakness

Unexplained fatigue and weakness are some of the first signs of pediatric heart failure. When the body’s organs are not receiving oxygen and nutrients due to poor blood flow, symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and low energy can occur. Children may have difficulty engaging in play or sports due to extreme tiredness.
Warning Sign 2: Rapid Breathing or Difficulty Breathing

Rapid breathing, or difficulty breathing, is a hallmark symptom of heart failure in children. When the heart is not pumping blood properly, fluid can accumulate in the lungs, leading to breathing difficulties. This may be accompanied by shortness of breath, especially during physical activity or while lying down. Babies may show signs of labored breathing or irregular chest movements.
Warning Sign 3: Swelling in the Legs, Abdomen, or Face
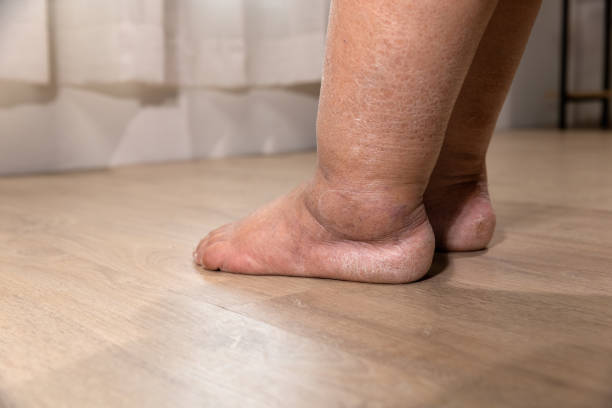
If the heart fails to pump the blood properly, it results in the accumulation of fluids within the body and hence it causes swelling, especially in the lower limbs, abdomen or face. This is known as edema and can be a sign of heart failure’s progression. Swelling around the abdomen may also cause discomfort and difficulty in feeding, particularly in infants.
Warning Sign 4: Poor Feeding and Weight Gain

In infants and toddlers, poor feeding and poor weight gain are common indicators that may be seen in cases of heart failure. Inability to pump blood by the heart implies that less blood reaches the digestive tract. Children with heart failure may tire easily when being fed. They fail to gain proper nutrition.
Warning Sign 5: Persistent Coughing or Wheezing

Fluid accumulation in the lungs in children with heart failure can cause coughing or wheezing. Fluid accumulation within the tissues of the lungs happens when the pumping function of the heart is compromised. The cough, in most cases, is dry, persistent, and exacerbated when one is physically active or when sleeping.
Unsure how pediatric cardiologists diagnose heart failure in children? Let’s dive into the diagnostic process and the tests involved.
How Pediatric Cardiologists Diagnose Heart Failure in Children

Clinical Evaluation
The diagnostic process begins with a thorough clinical evaluation, where the pediatric cardiologist reviews the child’s symptoms, medical history, and growth patterns. A physical examination focuses on identifying signs such as fatigue, swelling, or abnormal heart sounds.
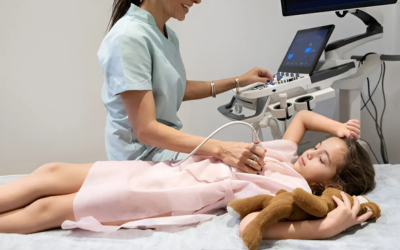
Echocardiography (2D/3D)
A 2D echocardiogram provides a detailed view of the heart’s structure and function, identifying any structural heart defects and assessing how well the heart pumps blood.
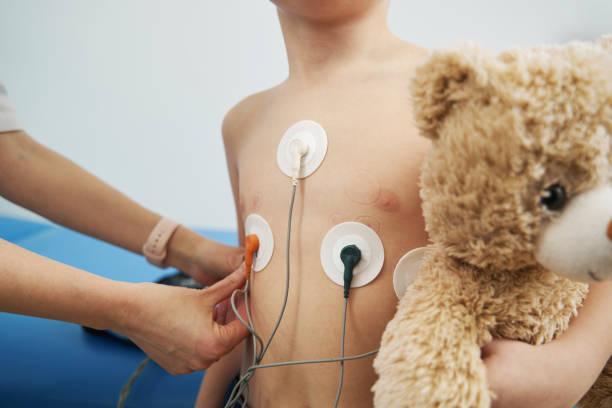
Electrocardiogram
An ECG records the electrical activity of the heart, helping to identify abnormal heart rhythms that may be contributing to heart failure.
Chest X-ray and Blood Tests
Chest X-rays help detect fluid buildup in the lungs, while blood tests can reveal underlying causes such as infection, anemia, or kidney problems.
Wondering how pediatric heart failure is treated? Here are the treatment options that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Treatment and Management Options for Pediatric Heart Failure
- Medications
Medications like diuretics, ACE inhibitors, and beta-blockers help reduce fluid buildup, lower blood pressure, and improve heart function.
- Lifestyle Modifications
A balanced diet, managing salt intake, and adequate rest are necessary for managing heart failure in children.
- Cardiac Surgery or Interventions
In severe cases, surgical interventions or catheter-based procedures may be needed to correct congenital heart defects or improve heart function.
- Cardiac Rehabilitation
After stabilization, children may benefit from a rehabilitation program to improve heart strength and endurance.
Conclusion
Recognizing the warning signs of pediatric heart failure early can make all the difference. Timely intervention, appropriate treatment, and ongoing care are crucial to improving outcomes and ensuring a better quality of life. Dr. Prashant Bobhate’s approach combines advanced diagnostics, personalized treatment plans, and compassionate care to help children with heart failure live healthier, more active lives.
FAQs
Can children live a normal life with heart failure?
What is the treatment for pediatric heart failure?
Treatment includes medications like diuretics, ACE inhibitors, and beta-blockers, along with lifestyle adjustments and possible surgery.
What are the risks of pediatric heart failure?
Without treatment, pediatric heart failure can lead to severe complications, including heart failure, lung damage, and poor growth.
Can heart failure in children be prevented?
While some heart defects cannot be prevented, early detection and intervention can prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Is pediatric heart failure the same as adult heart failure?
No, pediatric heart failure often results from congenital defects, while adult heart failure is usually due to heart disease or lifestyle factors.